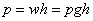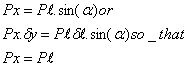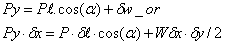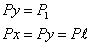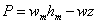Hydrostatic
Hydrostatic is the branch of fluid mechanics which is concerned with fluids at rest. As stated previously, no tangential or shear stress exists between stationary fluid particles.
Thus in hydrostatic, all forces act normally to a boundary surface and are independent of viscosity. As a result, the controlling laws are relatively simple, and analysis is based on a straightforward application of the mechanical principles of force and moment. Solutions are exact with no need to have recourse to experimentation.
Diesel engine Vertical Turbine multistage centrifugal inline shaft water Drainage Pump This kind of vertical drainage pump is mainly used for pumping no corrosion, temperature less than 60 °C, suspended solids (not including fiber, the grits) less than 150 mg/L content of the sewage or waste water. VTP type vertical drainage pump is in VTP type vertical water pumps, and on the basis of the increase and the collar, set the tube oil lubrication is water. Can smoke temperature below 60 °C, send to contain a certain solid grain (such as scrap iron and fine sand, coal, etc.) of sewage or waste water.

Pressure intensity
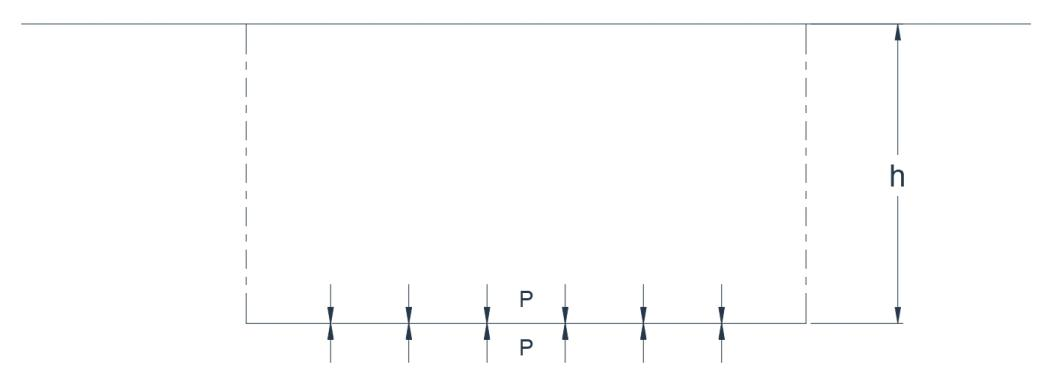
The pressure intensity or, more simply, the pressure on a surface is the pressure force per unit area. In Figure 4, the vertical downward pressure force acting on the horizontal
lamina is equal to the mass of the prism of fluid vertically above it, plus the pressure intensity at the interface with another fluid. For static equilibrium there must be a corresponding upward vertical pressure below the lamina. In the case of an incompressible liquid in contact with the atmosphere, the gauge pressure p (in pascals) is given by
where w is the specific mass of the liquid and h is the depth below the free surface. The latter is referred to as the pres-
Fig.4.Pressure forces on a submerged horizontal lamina
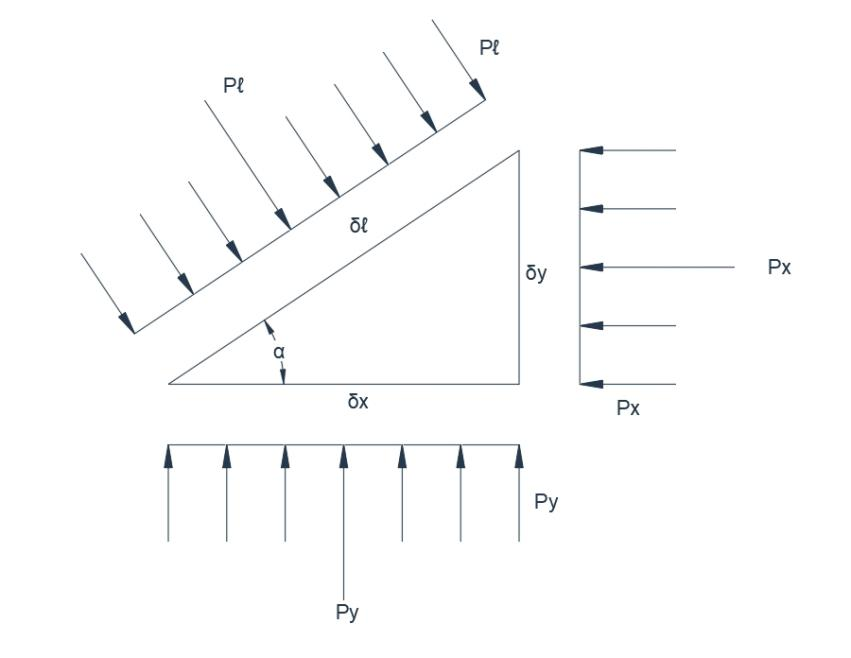
sure head and is generally stated in metres of liquid. The form of the equation shows that the pressure increases linearly with depth. As gravity is the physical property which is involved, the free surface of a still liquid is always horizontal and the pressure intensity is the same on any horizontal plane within the body of the liquid. Moreover, it may be shown that the pressure intensity on any elemental particle is the same in all directions. This follows from a consideration of the pressure forces acting on an elemental triangular-shaped prism(Fig.5) of unit horizontal length, with sectional dimensions δl,δx,δy,and mass δw.
Fig.5.Pressure forces on a submerged triangular-shaped prism
For equilibrium in the horizontal direction,
Similarly in the vertical direction,
neglecting second-order terms of very small quantities,
Thus The pressure intensity is therefore independent of the angle of inclination of the elemental surface and is the same in all directions.
Pressure measurement
Types of device
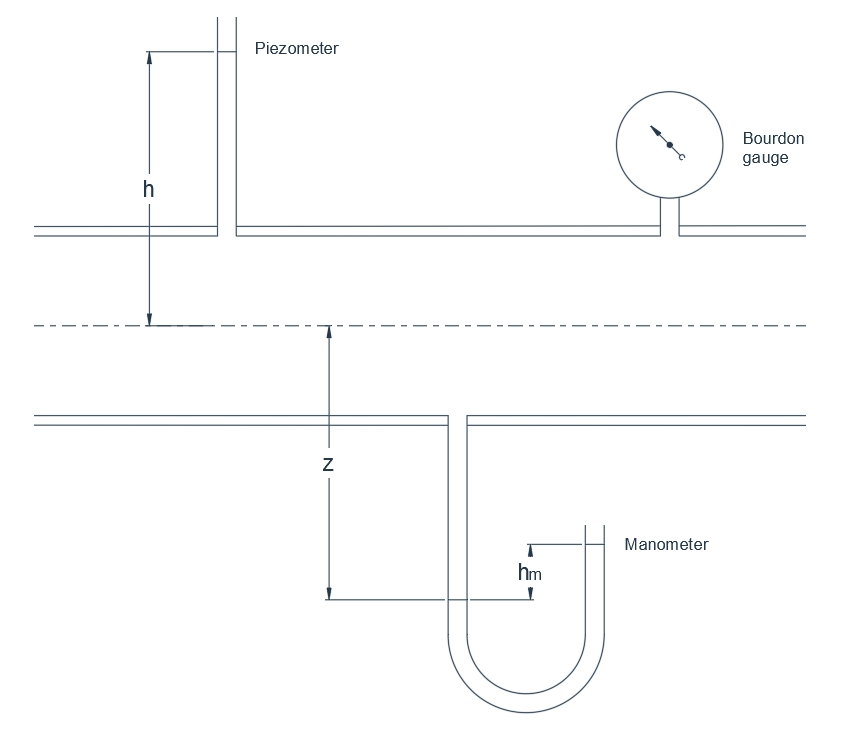
In the case of liquids with a free surface, the pressure at any point is represented by the depths below the surface.When the liquid is totally enclosed, as in pipes and pressure conduits, the pressure cannot readily be ascertained and a suitable measurement device is required. There are three principal types:(a) piezometer,(b) manometer,and (c) Bourdon gauge. These are shown fitted to a pipeline in Figure 6.

Vacuum Priming well point pump
Model No:TWP
TWP series Movable Diesel Engine self-priming Well point Water Pumps for emergency are joint designed by DRAKOS PUMP of Singapore and REEOFLO company of Germany . This series of pump can transport all kinds of clean, neutral and corrosive medium containing particles. Solve a lot of traditional self-priming pump faults. This kind of self-priming pump unique dry running structure will be automatic startup and restart without liquid for first start, The suction head can be more than 9 m; Excellent hydraulic design and unique structure keep the high efficiency more than 75%. And different structure installation for optional.
Piezometer
If a tapping is made in the boundary surface and a sufficiently long tube connected, the liquid will rise in the tube until balanced by atmospheric pressure. The pressure in the main body of the liquid is represented by the vertical height of the liquid column. Clearly, the device is only suitable for moderate pressures, otherwise the liquid will rise too high in the piezometer tube for convenient measurement.
Fig.6.Pressure measurement devices
When the liquid is flowing, the piezometer tapping should not exceed 3 mm diameter and should be flush with the boundary surface. For greater accuracy, a piezometer ring may be fitted.This consists of an annular chamber surrounding the pipe and connected to it by a number of equally spaced tappings.
Manometer
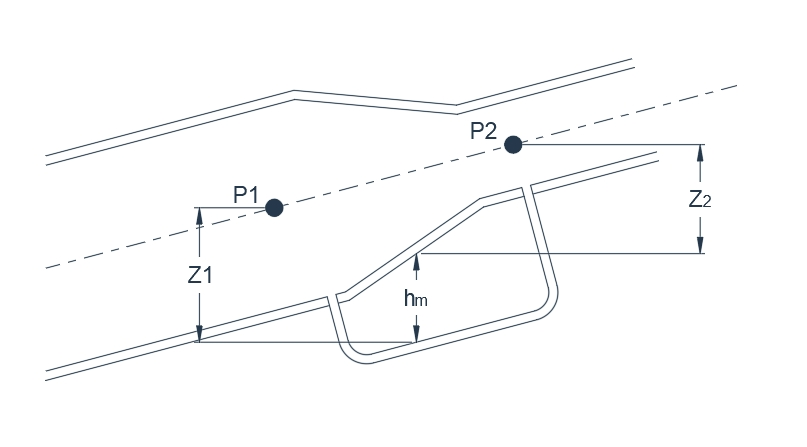
Manometer The principle is the same as that described above, but the difficulties associated with an excessively long tube are overcome by fitting a U-tube containing an immiscible liquid. Mercury(specific gravity 13,6) is the manometer liquid usually employed for measuring water pressure. The gauge pressure p in the pipeline is given by
Where
h= the difference in level of the manometer liquid in the two limbs,
z=the height of the pipe centre line above the meniscus in the limb on the pipe side,and
w, wm = the specific mass of the pipe and manometer liquids respectively.
wing to the fluctuating positions of the menisci, direct calibration is not possible. However, this may be achieved if the limb on the pipe side is greatly enlarged so that the level of the meniscus remains virtually constant. Pressures can then be read off a graduated scale attached to the other limb.
Fig.7. Differential manometer
A quantitative evaluation of pipe flow is often based on a measurement of pressure difference between nearby tappings. A differential manometer (Fig.7) is employed and the manometer liquid is usually mercury. When the pressure differences are small, a lighter immiscible liquid will yield more accurate results.
The pressure difference pt- pzis given by
where the symbols have the same meaning as in Equation 6. If the pipe is horizontal,
Differential manometers of a more intricate nature have been devised to meet the specific needs of commercial and laboratory practice.
Bourdon gauge
This is a commercial instrument which is fitted either directly to the pipe itself or to the end of a piezometer line. It consists of a bent tube suspended freely in the curved portion and held rigidly at the stem. An increase in internal pressure tends to straighten the tube and, as the deflection is directly proportional to the applied pressure, a simple mechanism enables the latter to be directly recorded. Since the pressure on the outside of the tube is atmospheric, a gauge pressure is registered and this is normally applicable to the centre point of the instrument.
The Bourdon gauge is useful as a general indicator of pressure but is not suitable where considerable accuracy is demanded, as is generally the case when differential pressures are to be measured.
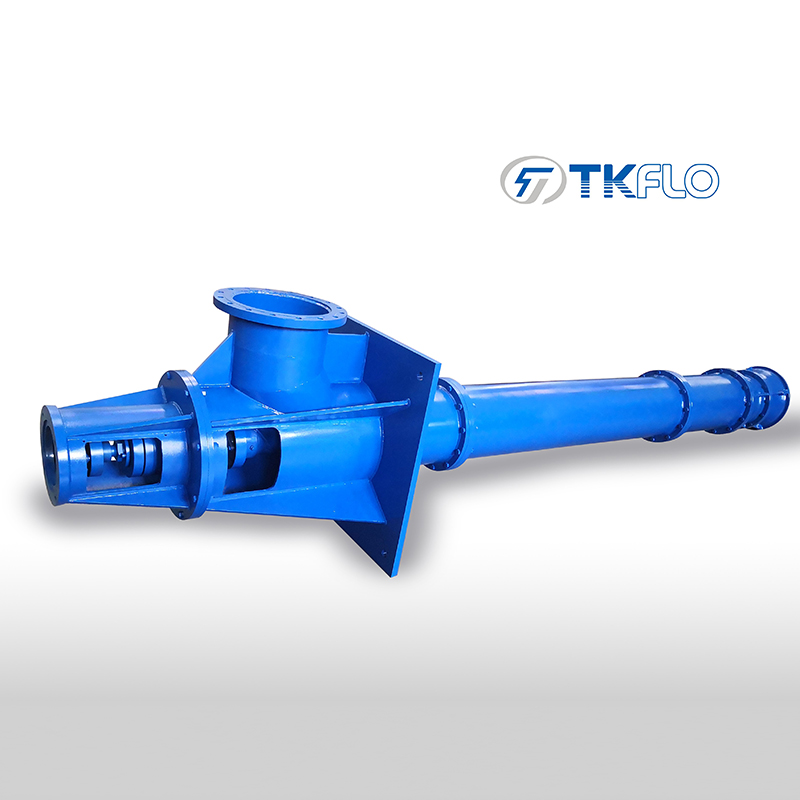
Model No:XBC-VTP
XBC-VTP Series vertical long shaft fire fighting pumps are series of single stage, multistage diffusers pumps, manufactured in accordance with the latest National Standard GB6245-2006. We also improved the design with the reference of the standard of United States Fire Protection Association. It is mainly used for fire water supply in petrochemical, natural gas, power plant, cotton textile, wharf, aviation, warehousing, high-rising building and other industries. It can also apply to ship, sea tank, fire ship and other supply occasions.
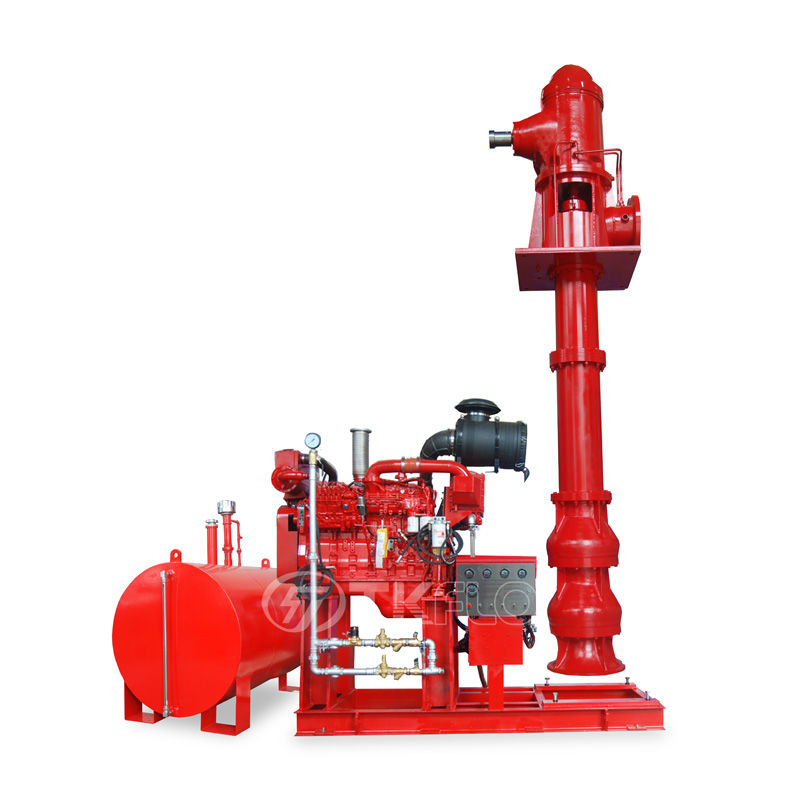
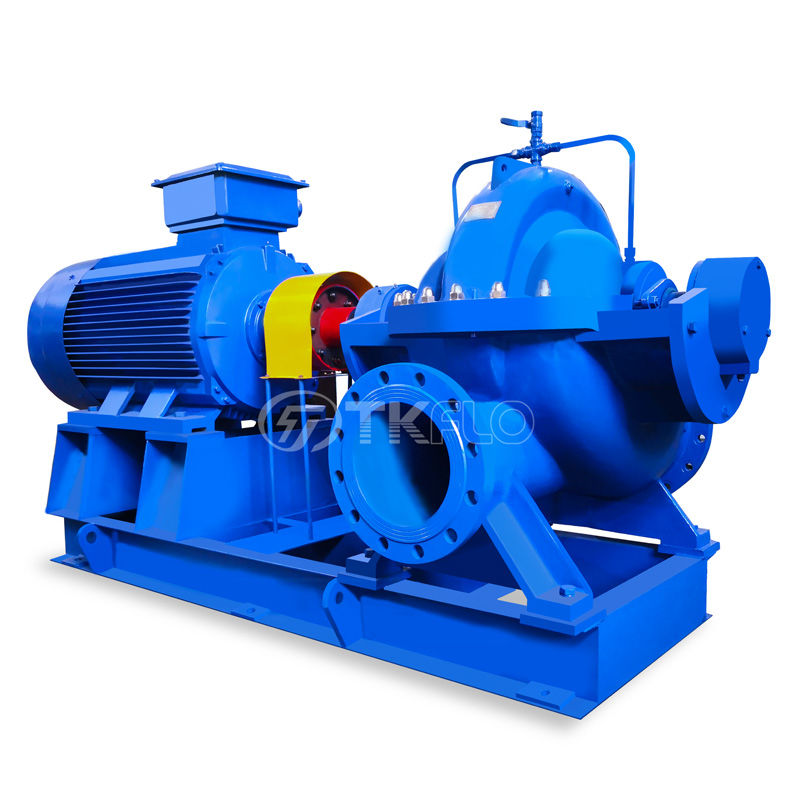


Centrifugal Sea Water Destination Pump
Model No:ASN ASNV
Model ASN and ASNV pumps are single-stage double suction split volute casing centrifugal pumps and used or liquid transportation for water works, air-conditioning circulation, building, irrigation, drainage pump station, electric power station, industrial water supply system, fire-fighting system, ship, building and so on.
Post time: Mar-25-2024
 seth@tkflow.com
seth@tkflow.com