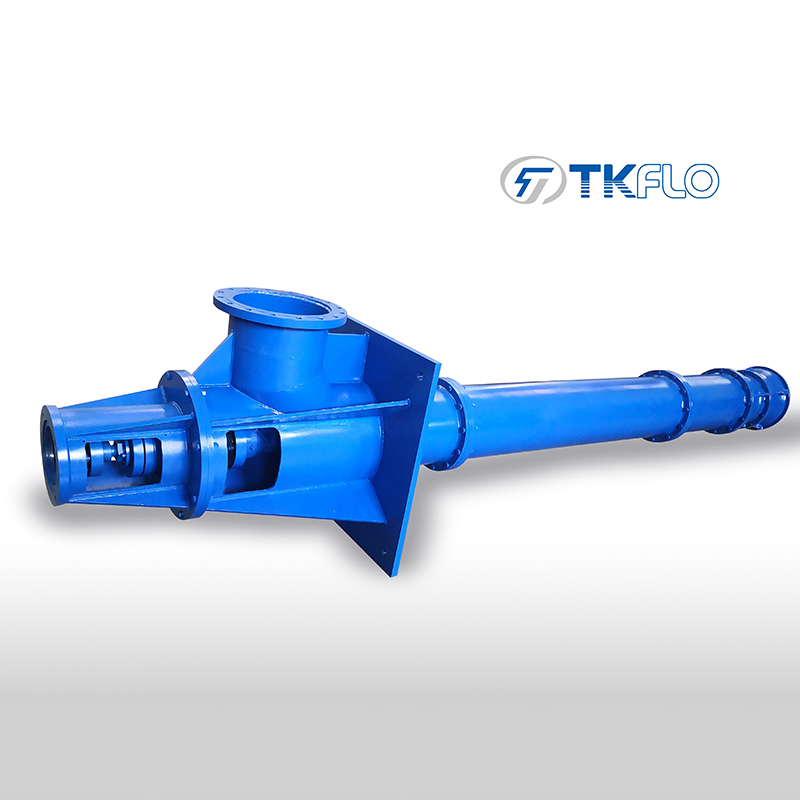
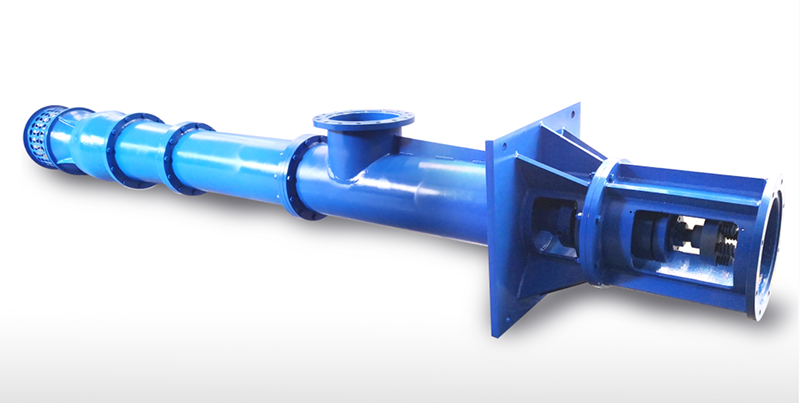
Material of Vertical Turbine Pump
Bowl: Cast iron, Stainless steel
Shaft: Stainless steel
Impeller: Cast iron, Bronze or Stainless steel
Discharge head: Cast iron or carbon steel

Pump advantage
√ Corrosion resistance main part material, famous brand bearing, thordon bearings suitable for sea water.
√ Excellent design for high Efficiency save energy for you.
√ Flexible installation method suitable for different site.
√ Stable running, Easy to install and maintain.
1. The inlet shall be vertical downward and the outlet horizontal above or under the base.
2. The impeller of pump is classified into enclosed type and half-opening type, and three adjustments: non-adjustable, semi adjustable and full adjustable. It is unnecessary to fill the water when the impellers are fully immersed in the pumped liquid.
3. On the basis o Pump, this type is additionally fit with muff armor tubing and the impellers are made of abrasive resistant material, widening the applicability of pump.
4. The connection of impeller shaft, transmission shaft, and motor shaft applies the shaft coupling nuts.
5. It applies water lubricating rubber bearing and packing seal.
6. The motor generally applies standard Y series tri-phase asynchronous motor, or YLB type tri-phase asynchronous motor as requested. When assembling Y type motor, the pump is designed with anti- reverse device, effectively avoiding reverse of pump.
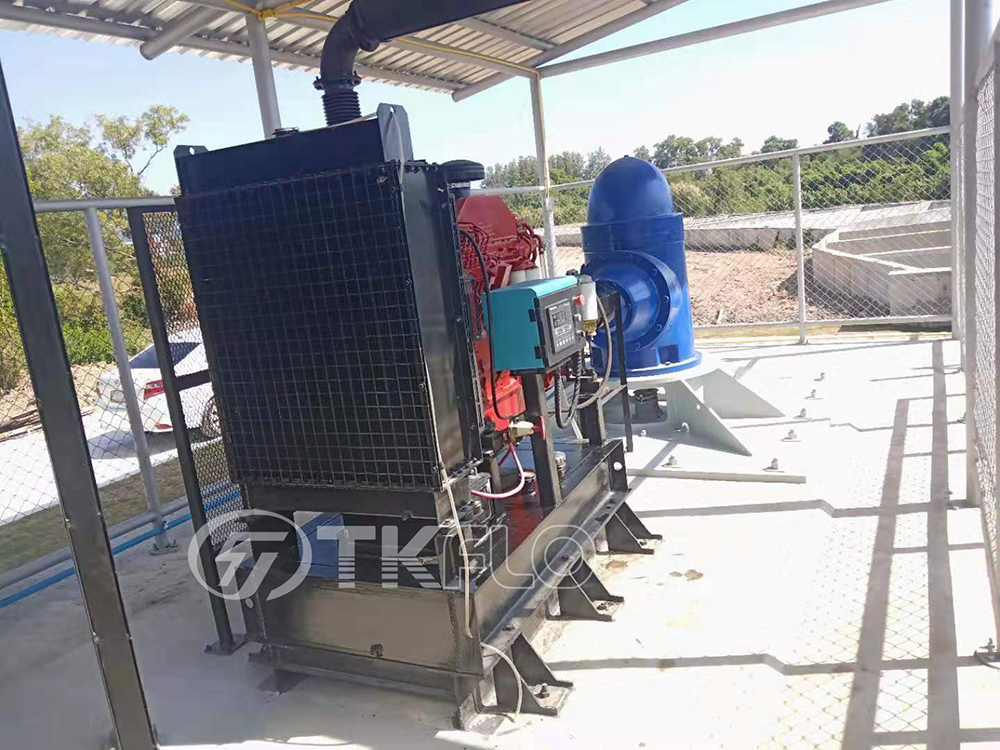



※ More detail about our VTP series Long Shaft Vertical Turbine Pump for curve and dimension and data sheet please contact Tongke.
How It Works
The vertical turbine pump is normally driven by an AC electric induction motor or a diesel engine via a right angle drive. The end of the pump consists of a rotating impeller that is joined to a shaft and guides the well water into a diffuser casing known as a bowl.
Pumps with multi-stage arrangements use several impellers on a single shaft to generate higher pressure that would be required for pumping water from deeper wells or where higher pressure (head) is required at ground level.
A vertical turbine pump works when water comes through the pump from the bottom through a bell-shaped device known as a suction bell. The water then moves into the first stage impeller, which increases the velocity of the water. The water then moves into the diffuser casing directly above the impeller, where the high velocity energy is transformed into high pressure. The diffuser casing also guides the fluid into the next impeller located directly above the diffuser casing. The process goes on through all the stages in the pump.
The VTP pump line is normally designed to operate in wells or sumps. Its bowl assembly consists primarily of a suction case or bell, one or more pump bowls and a discharge case. The pump bowl assembly is positioned in the sump or well at a depth to provide the proper submergence.
FAQS
Solid shaft Pump
The shaft extension typically has a circular key way to pass on pump thrust, and a radial key way to transmit torque. The lower end coupling of the pump motor and the pump shaft is seen more often in tanks and shallow pumps, rather than deep-well operations.
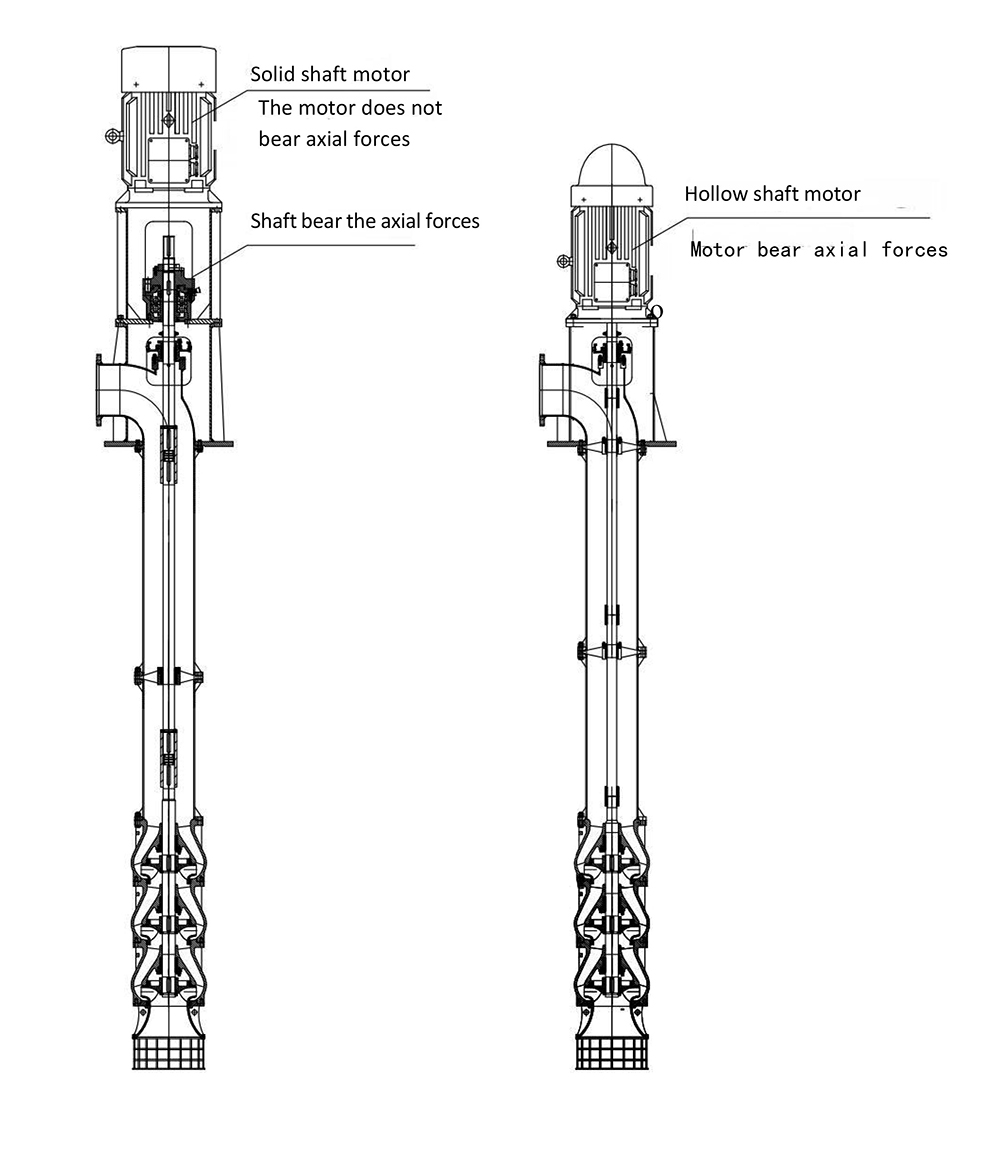
What are the Differences Between Vertical Hollow Shaft (VHS) Pump Motors vs. Vertical Solid Shaft (VSS)?
The pumping industry was revolutionized with the creation of the vertical pump motor in the early 1920' s. This allowed for electric motors to be attached to the top of a pump, and the impacts were impressive. The installation process was simplified, and because it required fewer parts, was then less expensive. The efficiency of the pump motors increased by 30%, and because vertical pump motors are purpose specific, they are more durable and reliable than their horizontal counterparts. Vertical pump motors are generally classified by their shaft type, either hollow or solid.
Construction Features
Both types of pump motors are explicitly designed to operate vertical turbine pumps, and they typically have a P-base mount without feet. The construction features of vertical pump motors influence their application and maintenance needs.
Hollow Shaft
The most obvious difference between the two types of pump motors is that one has a hollow shaft, which changes its construction features from that of a solid shaft. In hollow shaft pump motors, the pump head-shaft extends through the motor shaft and is joined at the motor's crest. An adjusting nut is located on the peak of the head-shaft which streamlines the regulation of the pump impeller strength. A steady bushing is often installed to stabilize and center the pump shaft in the motor shaft. When started, the pump shaft, motor shaft, and steady bushing rotate concurrently, resulting in a mechanical stability comparable to that of a solid shaft motor. Vertical hollow shaft pump motors are the most commonly used motor for deep-well pumps, but they are also being selected for any pump operation that requires easy adjust-ability.
Solid Shaft
Vertical solid shaft pump motors are connected to the pump shafts near the bottom end of the motor. The shaft extension typically has a circular keyway to pass on pump thrust, and a radial keyway to transmit torque. The lower end coupling of the pump motor and the pump shaft is seen more often in tanks and shallow pumps, rather than deep-well operations.
Vertical Turbine Pump Installation Type
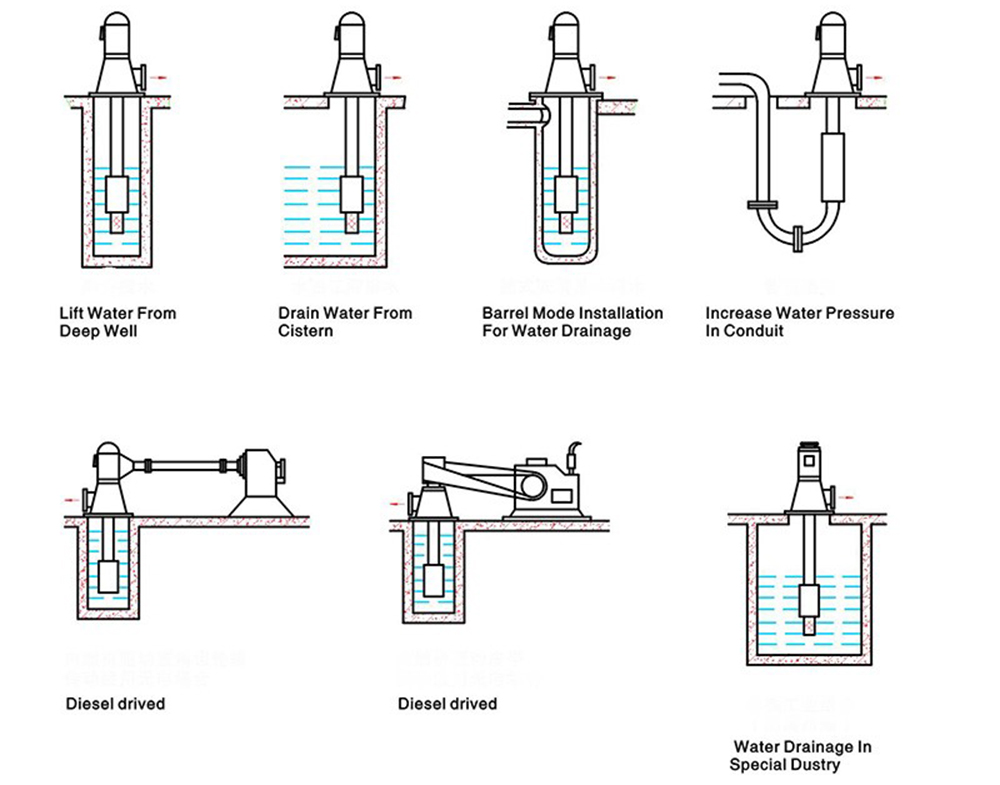
Notes Before Order
1. The temperature of medium shall not be higher than 60 .
2. The medium shall be neutral and PH value between 6.5~8.5. If the medium is not consistent to the requirements, specify in the order list.
3. For VTP type pump, the content of suspended substances in the medium shall be less than 150 mg/L; for VTP type pump, the max. Diameter of solid particles in the medium shall be less than 2 mm and the content less than 2 g/L.
4. VTP type pump shall be connected with clean water or soapy water outside to lubricate the rubber bearing. For two stage pump, lubricant pressure shall not be less than operational pressure.
Application
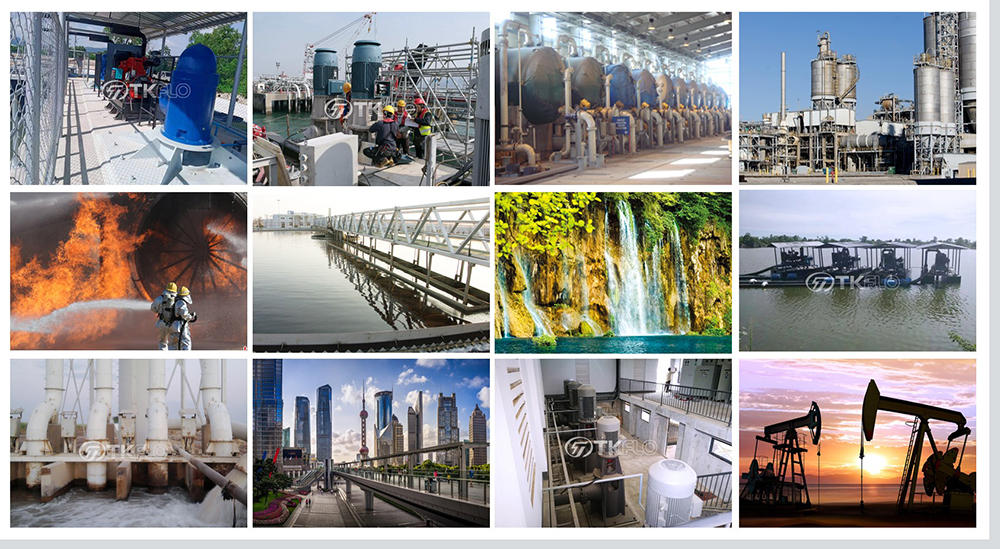
Vertical turbines are commonly used in all types of applications, from moving process water in industrial plants to providing flow for cooling towers at power plants, from pumping raw water for irrigation, to boosting water pressure in municipal pumping systems, and for virtually every other imaginable pumping application. Turbines are one of the most popular types of pumps for designers, end-users, installing Contractors, and distributors.

|
Commercial/Industrial/ Dewatering |
Water Parks/River/Sea Water Circulation |
|
Waster Plants/Agricultural Irrigation/Cooling Tower |
Flood Control/Municipal/Golf Courses/Turf Irrigation |
|
Mining/Snowing/Fire-Fighting |
Petrochemical Industry pump/Seawater desalination plant or salt water pump |
|
Municipal engineering/City flood control and drainage |
Industrial architecture/ Sewage treatment engineering |
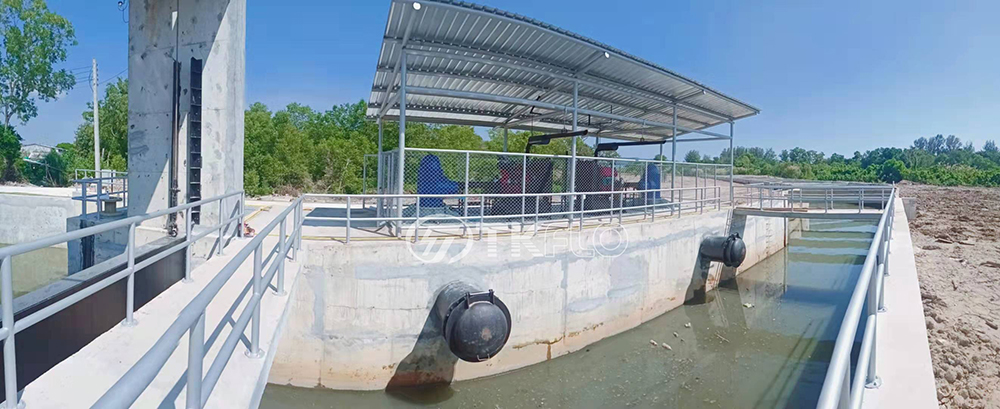
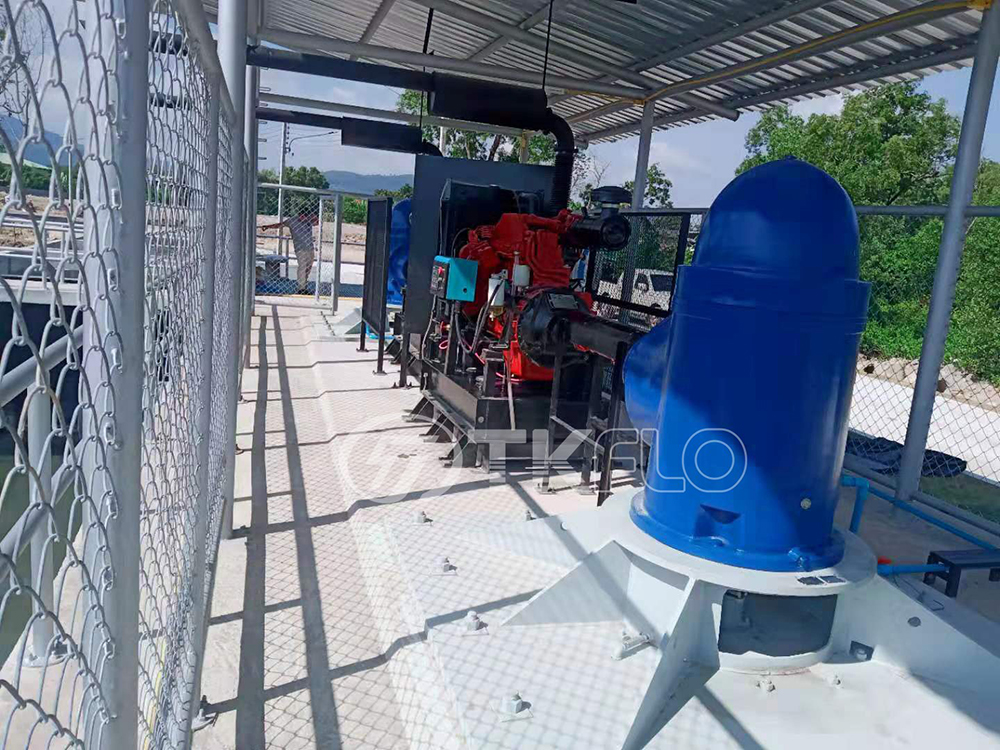
Sample project

Curve
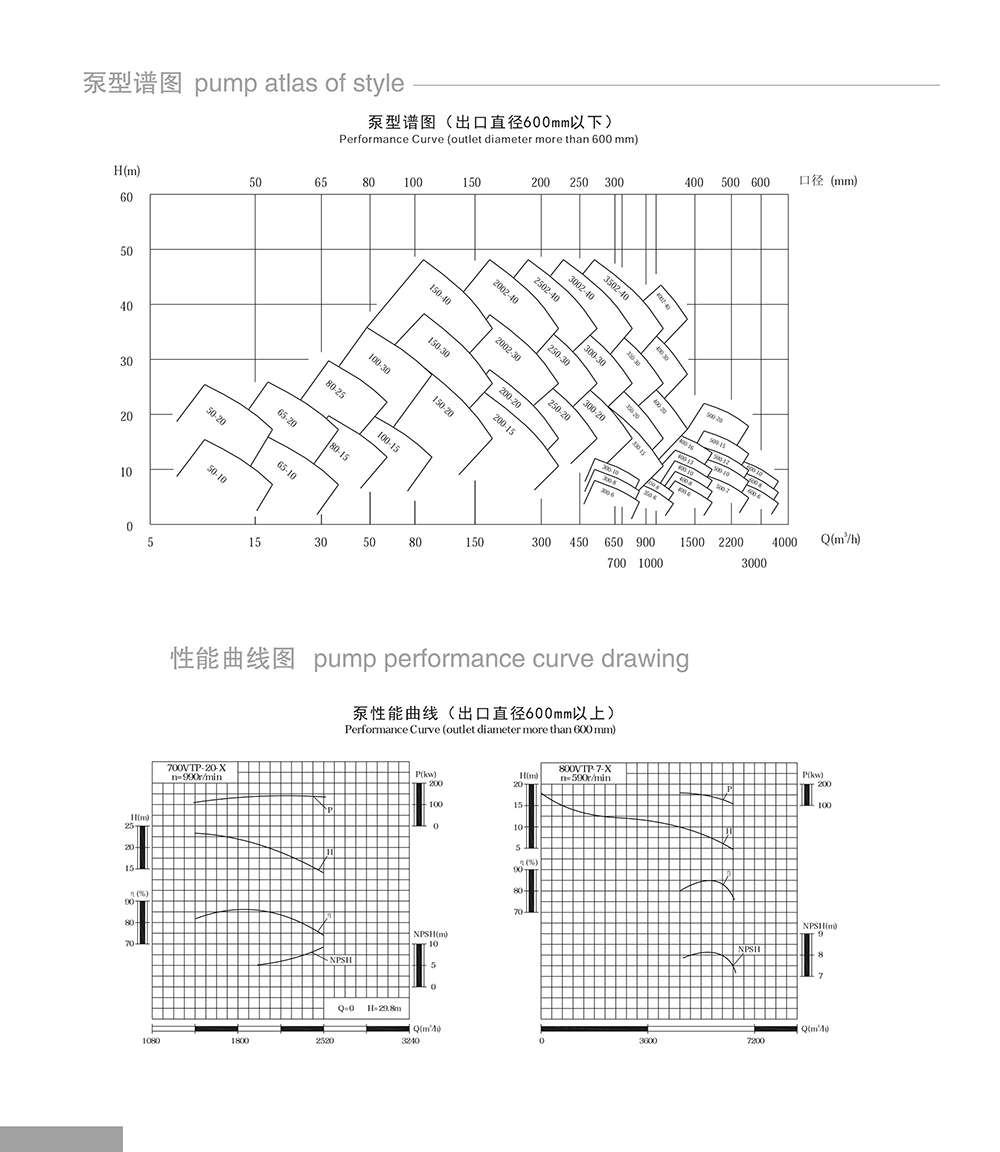
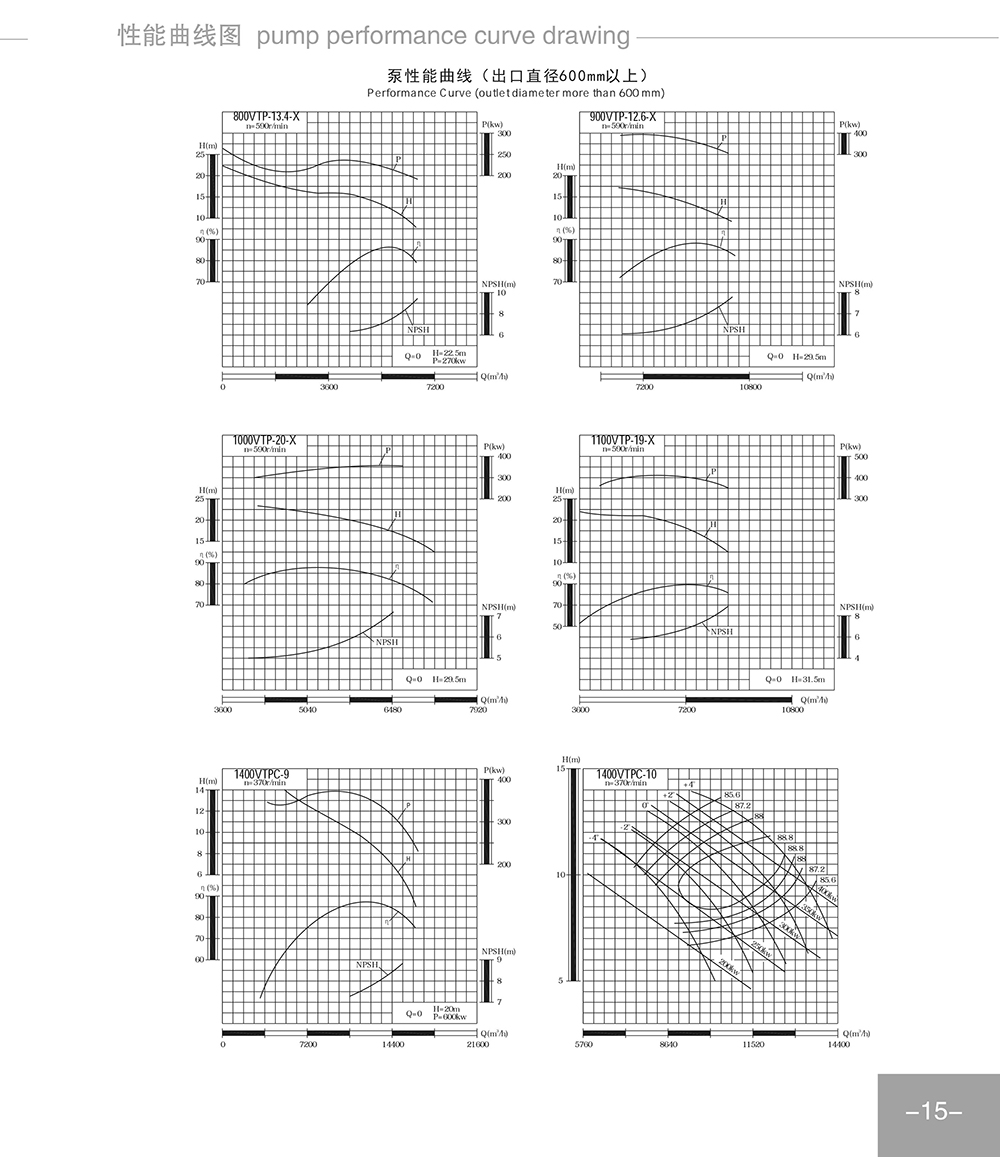
 seth@tkflow.com
seth@tkflow.com 










